Difference between revisions of "Pap Smear"
| (5 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
*[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pap_test Wikipedia] | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pap_test Wikipedia] | ||
| + | <gallery mode="packed-hover" widths=240px heights=180px> | ||
| + | File:Pap.jpg | ||
| + | File:605109-04X.jpg | ||
| + | File:Image021.png | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
== DIY Pap smear == | == DIY Pap smear == | ||
| Line 21: | Line 26: | ||
The test kit consists of a test tube with a clear solution. The woman inserts a regular tampon for three to eight hours, a week before the onset of her menstruation cycle, and then removes the tampon and places it in the test tube. | The test kit consists of a test tube with a clear solution. The woman inserts a regular tampon for three to eight hours, a week before the onset of her menstruation cycle, and then removes the tampon and places it in the test tube. | ||
The clear liquid inside the tube is actually a special solution that protects and seals the cervical and vaginal cells on the tampon. South-African microbiologists Andreas Karas and Jonathan Keytel | The clear liquid inside the tube is actually a special solution that protects and seals the cervical and vaginal cells on the tampon. South-African microbiologists Andreas Karas and Jonathan Keytel | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Links''' | ||
| + | *[http://www.hst.org.za/news/new-cervical-cancer-test New cervical cancer test] | ||
| + | *[http://www.sevafrica.com/modules/health/article.php?health_newsid=984 On sevafrica] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Gynecological Tests --> | ||
| + | <div class="alertBox1"> | ||
| + | {| class="alert" | ||
| + | ! [[Pap Smear]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:Cytobrush 2.jpg|120px|left]] | ||
| + | |http://nursingcrib.com/medical-laboratory-diagnostic-test/papanicolaou-test-pap-smear/ | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |http://www.womenshealthsection.com/content/gynpcsp/gynpc001.php3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |http://sisbib.unmsm.edu.pe/bvrevistas/anales/v62_n4/historica_citoptologia.htm | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |http://www.historiadelamedicina.org/papanicolau.htm | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |http://www.womenshealthspecialists.org/health-information/HPV-Pap-Smears | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Pap smears are a highly successful method to screen for cancer and the precancerous changes. By intervening selectively, we have been able to significantly reduce the incidence of cervical cancer. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |http://www.yd-diagnostics.com/html/e_product_05_01.html | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |http://geosalud.com/VPH/interpretacion_citologia.html Interpretación Resultado de la Citología del Cuello Uterino | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/OBGYN_101/MyDocuments4/Text/Pap/PapSmears.htm | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[http://www.ginecoweb.com/0citologia.html la citología cervico-vaginal]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <!-- Gynecological Tests end --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:GynePunk]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:08, 6 May 2015
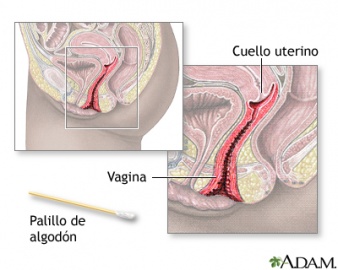
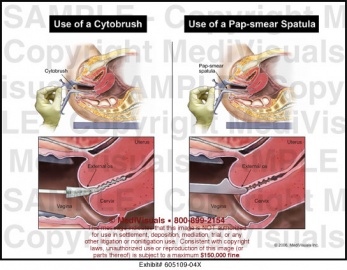
Pap Test or Papanicolaou Test
In Pap smear, a sample of loose cells is gently scraped from the cervix (the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina), spread on a glass slide, and sent to a laboratory for microscopic examination. A Pap smear is often done as part of a routine gynecologic examination in women, and is able to detect precancerous and cancerous conditions in their early and most treatable stages.
Alternatively, a new technique known as a liquid-based smear involves placing the scraped specimen into a vial of liquid. This liquid-based material is then studied under a microscope.
Purpose of the Pap Smear
- To check for cervical cell changes that could develop into cancer. It can also detect cancer cells.
- Performed regularly in women after age 18 to 21 (or in younger women who are sexually active) to screen for cancer of the vagina, cervix, and uterus.
- To detect benign cervical abnormalities, such as inflammation of the cervix.
Links
DIY Pap smear
- Sen-C-test:
The test kit consists of a test tube with a clear solution. The woman inserts a regular tampon for three to eight hours, a week before the onset of her menstruation cycle, and then removes the tampon and places it in the test tube. The clear liquid inside the tube is actually a special solution that protects and seals the cervical and vaginal cells on the tampon. South-African microbiologists Andreas Karas and Jonathan Keytel
Links
| Pap Smear | |
|---|---|
| http://nursingcrib.com/medical-laboratory-diagnostic-test/papanicolaou-test-pap-smear/ | |
| http://www.womenshealthsection.com/content/gynpcsp/gynpc001.php3 | |
| http://sisbib.unmsm.edu.pe/bvrevistas/anales/v62_n4/historica_citoptologia.htm | |
| http://www.historiadelamedicina.org/papanicolau.htm | |
| http://www.womenshealthspecialists.org/health-information/HPV-Pap-Smears | |
| Pap smears are a highly successful method to screen for cancer and the precancerous changes. By intervening selectively, we have been able to significantly reduce the incidence of cervical cancer. | |
| http://www.yd-diagnostics.com/html/e_product_05_01.html | |
| http://geosalud.com/VPH/interpretacion_citologia.html Interpretación Resultado de la Citología del Cuello Uterino | |
| http://www.brooksidepress.org/Products/OBGYN_101/MyDocuments4/Text/Pap/PapSmears.htm | |
| [la citología cervico-vaginal] |