Difference between revisions of "Low temperature sintered TiO2 porous layer"
Shihweichieh (talk | contribs) m (→Abstract) |
Shihweichieh (talk | contribs) m (→Abstract) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Abstract= | =Abstract= | ||
| − | Conventionally it requires 450˚C to 500˚C to sinter the TiO2 porous layer which functioning as the photo-electrode in dye sensitized solar cell. The high sintering temperature eliminates the participation of textile or plastic substrates in the DSSC making. Therefore, a low temperature sintering method to make the TiO2 layer is widely discussed. There are two | + | Conventionally it requires 450˚C to 500˚C to sinter the TiO2 porous layer which functioning as the photo-electrode in dye sensitized solar cell. The high sintering temperature eliminates the participation of textile or plastic substrates in the DSSC making. Therefore, a low temperature sintering method to make the TiO2 layer is widely discussed. There are two methods are applied: 1, Hot UV sintering with mercury tube and heat plate. 2, Chemical sintering with HCL additive. The TiO2 nano particles are purchased from a Taobao supplier. |
==HOT UV sintering== | ==HOT UV sintering== | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 21 October 2023
Contents
Abstract
Conventionally it requires 450˚C to 500˚C to sinter the TiO2 porous layer which functioning as the photo-electrode in dye sensitized solar cell. The high sintering temperature eliminates the participation of textile or plastic substrates in the DSSC making. Therefore, a low temperature sintering method to make the TiO2 layer is widely discussed. There are two methods are applied: 1, Hot UV sintering with mercury tube and heat plate. 2, Chemical sintering with HCL additive. The TiO2 nano particles are purchased from a Taobao supplier.
HOT UV sintering
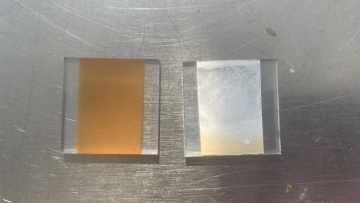
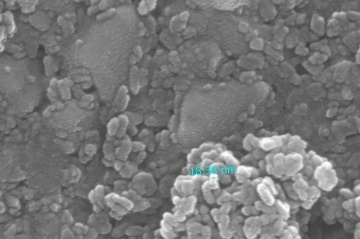
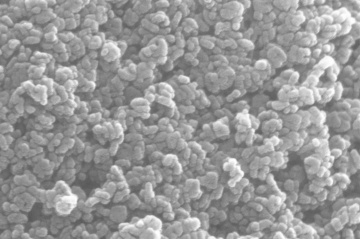
Two pastes was applied in this experiment. The first one is a commercial paste 18NR-T purchased from Greatcell Solar. Another self-made paste is made with 0.3 grams of TiO2 nano particles dissolved in 20ml of ethanol solvant. solution. Both paste are coated on FTO by doctor blade method. The Hot UV sintering was proceed for 18 hours, appearance of two pastes were compared. The self-made paste was sent to SEM and being analyzed.
- 150˚C sintering with UV assist
- SEM photos
Low temperature sintering TiO2 paste made with HCL
Firstly, a commercial low temperature sintering TiO2 purchased from a Japanese company peccell was used. This TiO2 paste costs JPY110,000 for 100 grams.
References
- Holliman, Peter J., Dhiyaa K. Muslem, Eurig W. Jones, Arthur Connell, Matthew L. Davies, Cecile Charbonneau, Matthew J. Carnie, and David A. Worsley. 2014. “Low Temperature Sintering of Binder-Containing TiO2/Metal Peroxide Pastes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells.” Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2 (29): 11134–43. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA01000K.
- Zen, Shungo, Yuta Ishibashi, and Ryo Ono. 2014. “Low-Temperature Sintering for Plastic Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells Using Conventional TiO2 Paste Containing Organic Binders.” Applied Physics Letters 104 (21): 213904. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4880117.
- Oh, Yeonjun, Sung-Nam Lee, Han-Ki Kim, and Jihoon Kim. 2012. “UV-Assisted Chemical Sintering of Inkjet-Printed TiO 2 Photoelectrodes for Low-Temperature Flexible Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells.” Journal of The Electrochemical Society 159 (10): H777–81. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.011210jes.
- Hansen, Niklas D J, Muhammet Toprak, Masato Maitani, and Yuji Wada. n.d. “MICROWAVE ASSISTED SYNTHESIS OF TITANIUM DIOXIDE ELECTRODES FOR USE IN POLYMER DSSC.”
- Fathy, Marwa, Hossam Hassan, Hoda Hafez, Moataz Soliman, Fuad Abulfotuh, and Abd El Hady B. Kashyout. 2022. “Simple and Fast Microwave-Assisted Synthesis Methods of Nanocrystalline TiO2 and rGO Materials for Low-Cost Metal-Free DSSC Applications.” ACS Omega 7 (19): 16757–65. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c01455.