Difference between revisions of "KOH/ microscopio"
From Hackteria Wiki
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| − | * [[3- Check the KOH slide immediately for a “fishy,” amine odor | + | * [[3- Check the KOH slide immediately for a “fishy,” amine odor; a strong fishy odor from the mix means vaginosis is present.]] |
* [[4- Cover each specimen with a cover slip to exclude air bubbles.]] | * [[4- Cover each specimen with a cover slip to exclude air bubbles.]] | ||
Revision as of 13:33, 21 November 2015
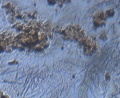
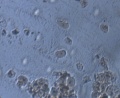
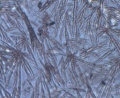
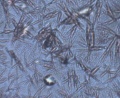
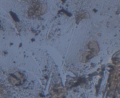
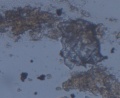
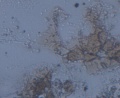
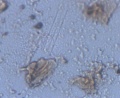
Microscopic observation of unfixed “wet mounts” of clinical specimens, either stained or unstained, can be useful for the rapid detection of the presence of bacterial, fungal, and parasitic organisms. Presumptive identification can be made, based on morphology and motility. The presence or absence of white blood cells and “clue cells” may also be demonstrated, and a number of well-recognized pathologic conditions may be identified.
Test Method Instructions
KOH slide. A sample of the vaginal discharge is placed on a slide and mixed with a solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH)10%. The addition of 10% KOH to the clinical specimen will dissolve tissue cells and keratinized material to allow better visualization of fungal elements.
- [[3- Check the KOH slide immediately for a “fishy,” amine odor; a strong fishy odor from the mix means vaginosis is present.]]
pre-p-KOH
- Error creating thumbnail: File missing