Difference between revisions of "Microscopy Station"
From Hackteria Wiki
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
[[File:micro01.jpg|400px]] | [[File:micro01.jpg|400px]] | ||
[[File:IMmicro02.jpg|400px]] | [[File:IMmicro02.jpg|400px]] | ||
| − | [[File:micro03.jpg|400px]][[File: | + | [[File:micro03.jpg|400px]] |
| + | [[File:micro04.jpg|400px]] | ||
| + | [[File:File:IMG_9784.JPG|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | experiment : | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KOH_test | ||
| + | Evaluation | ||
| + | |||
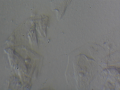
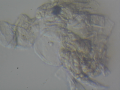
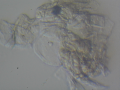
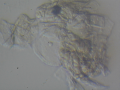
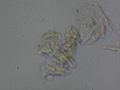
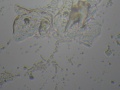
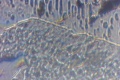
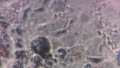
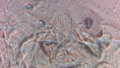
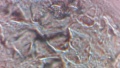
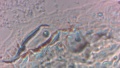
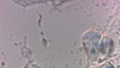
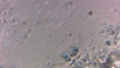
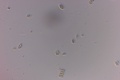
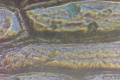
| + | Dermatophytes are easily recognized under the microscope by their long branch-like tubular structures called hyphae. Fungi causing ringworm infections produce septate (segmented) hyphae. Some show the presence of spores formed directly from the hyphae (arthroconidia). Under the microscope Tinea versicolor is recognized by curved hyphae and round yeast forms that give it a spaghetti-and-meatball appearance. Yeast cells appear round or oval and budding forms may be seen. The KOH prep cannot identify the specific organism; the specimen can be submitted for fungal culture to identify the organism. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A normal, or negative, KOH test shows no fungi (no dermatophytes or yeast). Dermatophytes or yeast seen on a KOH test indicate the person has a fungal infection. Follow-up tests are usually unnecessary. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The skin may be sore after the test because of the tissue being scraped off the top of the surface of the skin. | ||
[[File:micro04.jpg|400px]] | [[File:micro04.jpg|400px]] | ||
[[File:File:IMG_9784.JPG|400px]] | [[File:File:IMG_9784.JPG|400px]] | ||
| Line 96: | Line 110: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | |||
File:2015-05-15-085106.jpg | File:2015-05-15-085106.jpg | ||
Revision as of 01:10, 17 May 2015
golden edition microscope from pechblenda and rox fresh vaginal ( sep 2014, after Transhackfeminist)
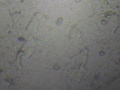
Here you can see first approach to the microscopic view of vaginal cells, we are working more into the shape/light to be allow investigate more around Cell Block Cytology and Its Efficacy in Diagnostic Cytology
ajcp.ascpjournals.org/content/114/4/599.full.pdf
- Pechblenda is building and trying to improve image shape and quality with HD web cam and many electronic mechanical waste at Hangar ....
- Experiment :
- Http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KOH test
- Evaluation
- A normal, or negative, KOH test shows no fungi (no dermatophytes or yeast). Dermatophytes or yeast seen on a KOH test indicate the person has a fungal infection. Follow-up tests are usually unnecessary.
- The skin may be sore after the test because of the tissue being scraped off the top of the surface of the skin.
- And some early examples of what we can see through
</gallery>
<gallery>